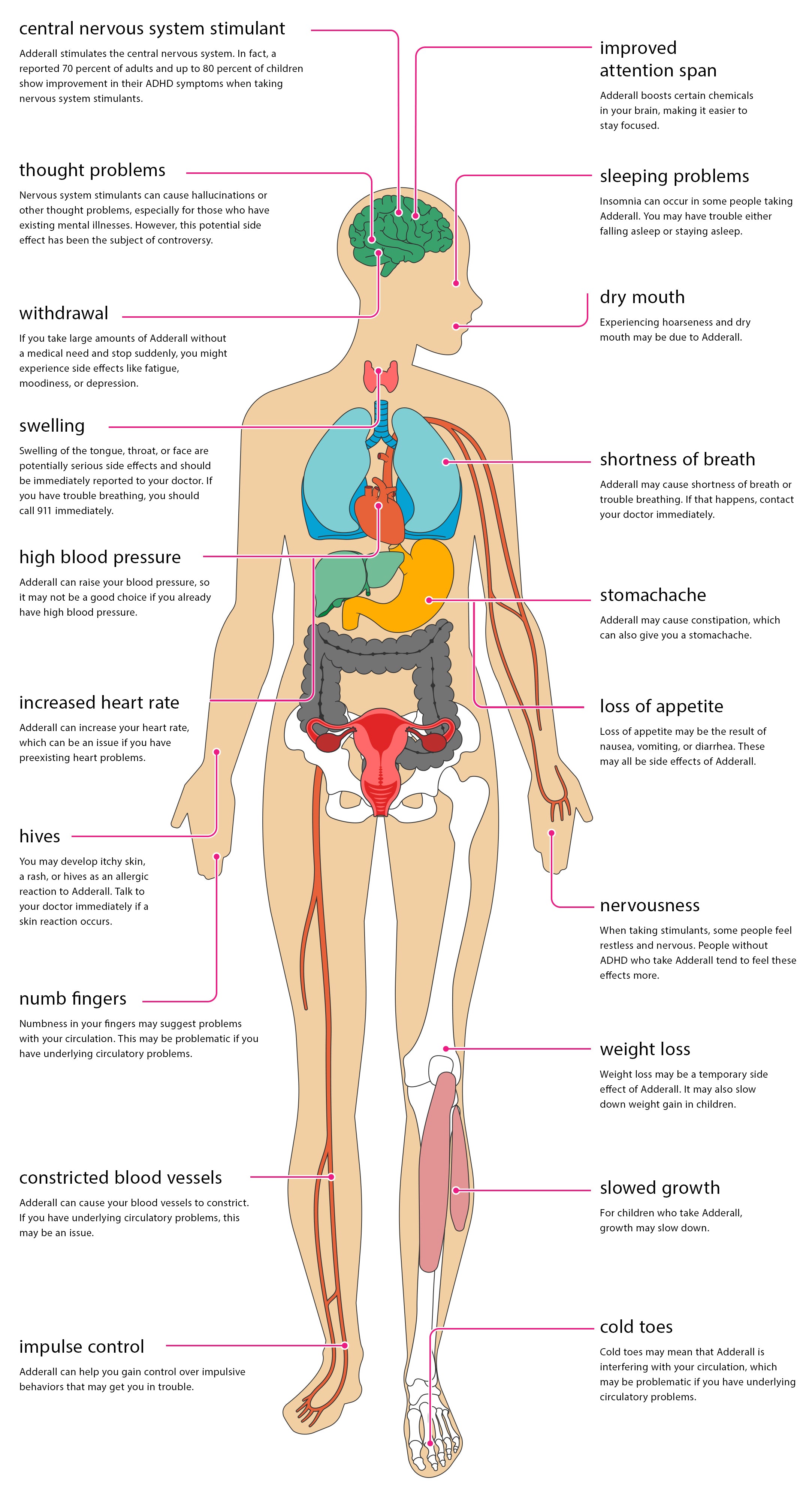
Adderall is a commonly prescribed medication for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. For many people, it helps improve focus, energy, and alertness. But because Adderall is a powerful central nervous system stimulant, it can also affect the body in significant ways — especially when taken without medical supervision.
This guide explains how Adderall works, its short- and long-term effects, and what you should know before taking it.
What Is Adderall and How Does It Work?
Adderall is a prescription medication that contains amphetamine and dextroamphetamine. These stimulants increase the activity of neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine, which play key roles in:
- attention
- impulse control
- mood regulation
- alertness
For people diagnosed with ADHD, Adderall can improve impulsivity, concentration, and hyperactivity. According to medical data, stimulant medications help 70–80% of children and around 70% of adults manage ADHD symptoms effectively — especially when combined with behavioral therapy.
Adderall is available as:
- Immediate-release tablets
- Extended-release (XR) capsules
Because it may interfere with sleep, it’s typically taken in the morning. Doctors usually begin with a low dose and adjust gradually.
Safety First: Before You Take Adderall
Before starting Adderall, your doctor needs to know:
- Any physical or mental health conditions
- All prescription or over-the-counter medications you take
- Your history with stimulants or substance use
Adderall is a federally controlled substance, meaning misusing it or taking it without a prescription can be dangerous.
How Adderall Affects the Body
Adderall influences multiple systems throughout the body — some effects can be helpful, while others may pose risks.
1. Effects on the Central Nervous System
When taken as prescribed, Adderall may help you feel more awake, focused, and calm. However, side effects can occur, including:
- nervousness or restlessness
- headaches
- dizziness
- dry mouth
- sleep disturbances
- changes in speech
- blurred vision
Sexual & Developmental Effects
- In children, Adderall may temporarily slow growth.
- Adults may notice changes in libido or sexual performance.
Serious Neurological or Psychiatric Effects
Seek medical help immediately if you experience:
- high fever
- severe weakness
- uncontrollable shaking or tics
- seizures
- hallucinations
- paranoia
- worsening depression or anxiety
These may signal dangerous reactions.
2. Withdrawal Symptoms (If Misused or Stopped Suddenly)
Stopping high doses of Adderall abruptly can cause withdrawal symptoms such as:
- extreme fatigue
- irritability or anxiety
- depression
- lack of energy
- panic attacks
- sleep problems (insomnia or oversleeping)
- intense hunger
- suicidal thoughts
- phobias or sudden panic
There’s no specific medical treatment — symptoms usually improve within days to weeks. Maintaining routine and proper rest can help.
3. Effects on the Cardiovascular & Respiratory System
As a stimulant, Adderall can affect your heart and blood vessels by:
- increasing heart rate
- raising blood pressure
- constricting blood vessels
This can lead to:
- cold, numb, or painful fingers and toes
- skin color changes (blue/red)
- circulatory issues
- Serious Heart-Related Risks
Call your doctor or emergency services immediately if you experience:
- chest pain
- shortness of breath
- irregular heartbeat
- fainting
In individuals with preexisting heart conditions, Adderall may increase the risk of heart attack, stroke, or sudden cardiac events.
4. Adderall and Alcohol: A Dangerous Combination
Mixing Adderall with alcohol can be extremely risky because:
- Adderall masks the feeling of being drunk
- This increases the risk of alcohol poisoning
- It places added stress on the heart, raising the chance of cardiovascular complications
Final Thoughts: Use Adderall Responsibly
Adderall can be highly effective for treating ADHD and narcolepsy when used under proper medical supervision. However, misusing Adderall or taking it without a prescription can lead to serious health risks.
Always follow your doctor’s guidance, monitor side effects, and avoid mixing stimulants with alcohol or other substances.